Smart Cities in Morocco: Blending Technology and Tradition
Morocco is a country that beautifully balances its rich history with the promise of a modern future. As urban populations grow and cities face increasing demands for sustainable infrastructure, Morocco is embracing the concept of smart cities. A smart city integrates advanced technology, data-driven solutions, and sustainable planning to improve urban life for residents, businesses, and visitors alike.
Smart Cities in Morocco are not just about technology—they represent a thoughtful blend of innovation and tradition. From intelligent traffic systems and digital government services to eco-friendly housing and renewable energy projects, these cities aim to enhance convenience, efficiency, and quality of life while preserving the cultural identity that makes Moroccan cities unique.
By focusing on modernization without erasing the past, Morocco is positioning itself as a pioneer in urban development in Africa. Smart cities here are designed not only to meet contemporary challenges such as population growth, traffic congestion, and climate change, but also to honor centuries-old architecture, vibrant medinas, and traditional marketplaces that continue to define the Moroccan urban experience.
For travelers, investors, and local residents, Morocco’s journey toward smart cities offers a fascinating glimpse into the future of urban living. It is a story of harmony—where cutting-edge technology coexists with history, culture, and heritage.
Morocco’s Vision for Smart Cities
Morocco’s approach to urban development goes beyond building modern infrastructure—it is a carefully crafted vision that aims to create cities that are both technologically advanced and culturally vibrant. The Moroccan government recognizes that the challenges of the 21st century—population growth, urban congestion, energy demands, and climate change—require innovative solutions. This has led to a national strategy focused on developing Smart Cities in Morocco that prioritize sustainability, efficiency, and quality of life.
At the heart of this vision is the concept of integrated urban planning. Morocco aims to create cities where technology streamlines daily life without sacrificing the rich heritage that gives each city its identity. For example, initiatives focus on smart mobility systems, digital government services, energy-efficient buildings, and environmental conservation—all designed to reduce urban pressure while maintaining the unique character of Moroccan neighborhoods.
Government programs, such as the National Urban Development Strategy and partnerships with private investors, have been key drivers in this transformation. These initiatives encourage innovation hubs, research centers, and technology parks, laying the foundation for cities that can accommodate modern industries, tourism, and creative enterprises. By fostering collaboration between public and private sectors, Morocco is ensuring that its smart city projects are both economically viable and socially inclusive.
Another essential part of Morocco’s vision is citizen-centric development. Smart city projects aim to enhance the quality of life for all residents by improving public services, providing accessible digital platforms, and promoting sustainable urban mobility. From renewable energy integration to real-time data monitoring for traffic and utilities, the government’s vision is a comprehensive roadmap for cities that are not only smart but also resilient and adaptable.
Ultimately, Morocco’s vision for Smart Cities in Morocco is about creating urban environments that balance modern technological solutions with traditional culture, ensuring that progress does not come at the cost of heritage. It’s a forward-looking approach that positions Morocco as a leader in sustainable and culturally conscious urban development in Africa.
Notable Smart City Projects in Morocco
Morocco’s commitment to building Smart Cities is visible through several high-profile projects across the country. These initiatives are designed to showcase how technology, sustainability, and culture can coexist in modern urban environments. Each project reflects Morocco’s strategy to balance innovation with tradition while addressing the challenges of rapid urbanization.
Casablanca Smart City Initiatives
Casablanca, Morocco’s largest city and economic hub, is leading the charge in urban innovation. The city has implemented intelligent traffic management systems, including smart traffic lights and real-time traffic monitoring, to ease congestion and reduce commute times. Additionally, Casablanca has invested in digital governance platforms, enabling residents to access administrative services online, from paying municipal fees to filing permits. Green urban planning is another focus, with public parks, eco-friendly buildings, and renewable energy integration demonstrating a commitment to sustainability.

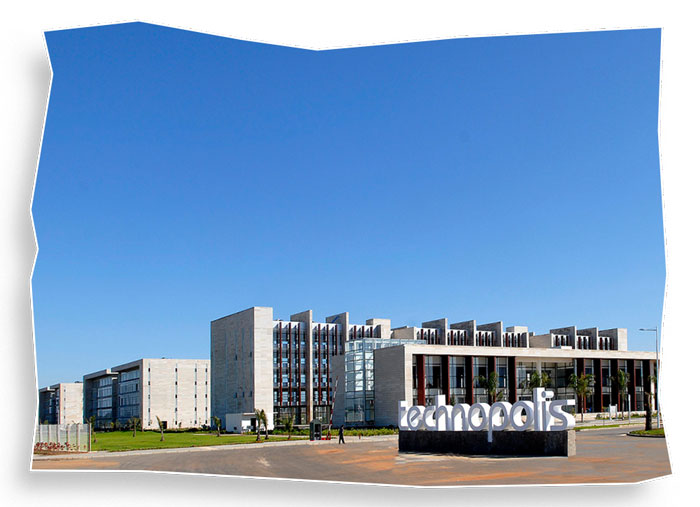
Rabat Technopolis
Rabat, the capital city, has embraced the smart city concept through its Technopolis project. Designed as a hub for research, technology, and innovation, Technopolis combines state-of-the-art infrastructure with modern business facilities. The project supports startups, encourages technology-driven education, and facilitates international partnerships. While Rabat modernizes its urban landscape, planners are careful to preserve historic neighborhoods and cultural landmarks, maintaining the city’s unique identity.

Zenata Smart City
Zenata, near Casablanca, is a prime example of a new city designed from the ground up with smart infrastructure in mind. The city incorporates renewable energy solutions, advanced waste management, and modern water treatment systems. Zenata also focuses on community-centered development, creating pedestrian-friendly streets, educational facilities, and cultural centers that reflect Morocco’s heritage. It is a living example of how Smart Cities in Morocco can integrate technology while respecting the environment and local culture.
These projects highlight Morocco’s diverse approach to smart city development. From revitalizing historic cities to constructing entirely new urban spaces, the country is demonstrating that technological innovation and cultural preservation can go hand in hand.
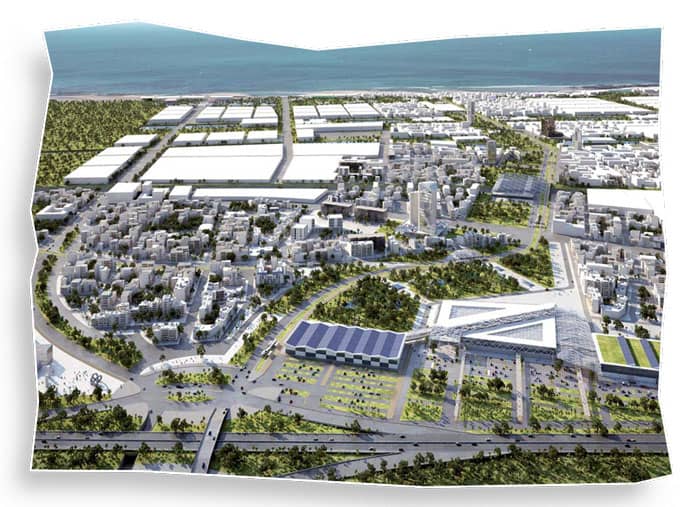
Mohammed VI Green City, Marrakech
In Marrakech, the Mohammed VI Green City project stands out as a model of sustainable urban development. Combining smart city technology with eco-friendly design, the project emphasizes energy-efficient buildings, waste recycling systems, and integrated public transport. Green corridors and parks are strategically placed to maintain natural habitats and provide residents with recreational spaces. By blending innovation with Marrakech’s traditional architectural aesthetics, the city sets a benchmark for environmentally conscious urban living.
Visit Morocco’s Smart Cities Today
Experience firsthand how history and modern innovation coexist. From eco-friendly streets to high-tech public services, Moroccan cities are redefining urban life.
Technology Transforming Urban Life
The core of Smart Cities in Morocco lies in the innovative technologies that make urban life more efficient, sustainable, and connected. From transportation and energy management to digital governance and public safety, Morocco is harnessing modern solutions to tackle the challenges of growing urban populations while enhancing the everyday experience of residents.
Smart Transportation
Transportation is one of the most visible aspects of Morocco’s smart city initiatives. Cities like Casablanca and Rabat are introducing intelligent traffic systems that monitor congestion in real time and adjust traffic lights to optimize flow. Electric buses and eco-friendly public transport networks reduce pollution and provide reliable alternatives to private vehicles. Ride-sharing apps and real-time transport tracking further improve convenience for commuters, making cities more accessible and reducing travel times.
Digital Government Services
Digitalization is transforming how Moroccan citizens interact with their government. Many smart city initiatives now offer e-services that allow residents to pay bills, request permits, and access municipal information online. These platforms reduce bureaucracy, increase transparency, and make city services more efficient. For businesses and investors, this digital infrastructure streamlines operations, contributing to Morocco’s reputation as a forward-looking economic hub.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Energy efficiency is a major component of Morocco’s smart city vision. Solar panels, smart grids, and renewable energy projects are being integrated into new buildings and public infrastructure. Cities like Zenata and the Mohammed VI Green City emphasize sustainable urban planning, combining green architecture with smart energy management to reduce carbon footprints. Water-saving technologies and intelligent waste management systems further support environmental sustainability.
Safety and Surveillance Innovations
Smart technologies also enhance safety in Moroccan cities. Real-time monitoring, surveillance cameras, and integrated emergency response systems help authorities respond quickly to incidents and maintain public security. Predictive analytics allow cities to identify and mitigate potential risks, from traffic accidents to environmental hazards, making urban areas safer for both residents and visitors.
By integrating these technologies, Morocco is creating cities that are not only smarter but also more livable. Residents experience more convenience and efficiency, businesses benefit from streamlined services, and cities can grow sustainably without compromising cultural heritage. This balance of technology and tradition is what makes Smart Cities in Morocco a model for urban development across Africa and beyond.
Preserving Tradition Amid Modernization
One of the most distinctive aspects of Smart Cities in Morocco is the country’s conscious effort to modernize urban spaces without erasing its rich cultural heritage. Moroccan cities are famous for their historic medinas, vibrant souks, traditional architecture, and centuries-old cultural practices. Smart city projects aim to integrate advanced technology while respecting these elements, creating urban environments where tradition and innovation coexist harmoniously.
Architectural Heritage
New developments in Moroccan smart cities carefully incorporate traditional design elements. For example, modern residential complexes and office buildings often feature Moroccan motifs, riad-style courtyards, and materials inspired by local architecture. This approach ensures that urban expansion does not compromise the aesthetic and historical character of cities like Marrakech, Fes, and Rabat.
Historic Preservation
Smart city initiatives prioritize the conservation of historic medinas and cultural landmarks. Urban planners use digital mapping and IoT monitoring to track the structural health of historic buildings, ensuring timely maintenance while minimizing disruption. In addition, technologies such as augmented reality and interactive apps are employed to enhance tourism experiences, allowing visitors to explore historic areas with modern tools without damaging delicate structures.
Cultural Engagement
Technology also supports the preservation and promotion of Moroccan culture. Smart platforms enable artisans to reach wider audiences, connecting traditional crafts with online marketplaces. Festivals, cultural events, and heritage tours are increasingly organized using smart tools that enhance accessibility and visitor engagement. By bridging digital innovation with cultural expression, Morocco ensures that its traditions remain vibrant in the 21st century.
Community-Centered Design
Smart city projects in Morocco emphasize community involvement in planning and decision-making. By consulting residents and local stakeholders, cities maintain a human-centric approach that respects social customs, neighborhood dynamics, and public spaces. This ensures that technological advancements enhance rather than disrupt daily life.
Through these efforts, Morocco demonstrates that modernization does not mean replacing tradition. Instead, Smart Cities in Morocco exemplify a forward-thinking model where technology serves as a tool to preserve and celebrate cultural heritage while creating sustainable, efficient, and livable urban spaces.
Challenges in Building Smart Cities
While Morocco is making impressive strides in developing Smart Cities in Morocco, the journey is not without challenges. Building technologically advanced urban spaces that honor tradition requires careful planning, substantial investment, and collaboration across multiple sectors. Understanding these challenges provides insight into both the complexity and potential of Morocco’s smart city initiatives.
Balancing Modernization and Heritage Preservation
One of the biggest challenges is ensuring that urban modernization does not compromise Morocco’s cultural and architectural heritage. Integrating modern infrastructure into historic neighborhoods requires sensitive planning. For example, installing smart traffic systems or high-speed internet in ancient medinas must be done without altering traditional layouts or damaging historic buildings. Achieving this balance requires innovative engineering and collaborative planning between architects, historians, and city officials.
Digital Divide
Technology-driven cities risk leaving behind segments of the population that lack access to digital tools. Ensuring equitable access to smart services—such as e-governance platforms, online education, or smart transport apps—is crucial. Morocco must address disparities in internet access, digital literacy, and affordability to ensure that smart city benefits are inclusive for all residents, not just tech-savvy or affluent communities.
Environmental and Infrastructure Challenges
Rapid urban expansion and smart infrastructure development can strain existing resources. Smart cities rely heavily on electricity, water management systems, and digital networks. Balancing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and integrating renewable resources are ongoing challenges. Furthermore, ensuring that new construction projects meet sustainability goals while accommodating population growth is a complex undertaking.
Policy, Investment, and Coordination
Developing smart cities requires coordinated efforts between government agencies, private investors, and technology providers. Securing funding for large-scale projects, navigating bureaucratic hurdles, and aligning stakeholders’ interests are significant challenges. Additionally, implementing regulations that ensure privacy, data security, and ethical use of technology is critical to building trust among residents.
Despite these obstacles, Morocco’s approach demonstrates that challenges can be addressed through innovation, planning, and collaboration. By learning from pilot projects, leveraging international expertise, and maintaining a citizen-centered focus, Morocco is steadily moving toward a future where Smart Cities in Morocco thrive without compromising culture, sustainability, or social equity.
Case Studies & Success Stories
To understand the real-world impact of Smart Cities in Morocco, it’s helpful to examine specific projects that showcase innovation, sustainability, and cultural integration. These case studies highlight how Moroccan cities are using technology to improve quality of life while maintaining a strong connection to heritage.
Zenata Smart City: A Model for Sustainable Living
Located near Casablanca, Zenata is a city designed from scratch with smart infrastructure at its core. The project emphasizes renewable energy, water management, and waste recycling systems. Streets are pedestrian-friendly, and green spaces are integrated throughout the city, creating a healthy urban environment. Zenata also focuses on community well-being by including schools, healthcare centers, and cultural facilities. By blending eco-conscious design with modern technology, Zenata demonstrates how Smart Cities in Morocco can be sustainable, livable, and culturally aware.
Casablanca Mobility Project
Casablanca’s mobility initiative illustrates the impact of technology on urban life. The city implemented an intelligent traffic management system, equipped with real-time monitoring and adaptive traffic signals. This reduced congestion, improved public transport efficiency, and lowered pollution levels. Mobile apps for commuters provide live updates on traffic conditions and public transport schedules, making the city more navigable and convenient for residents and visitors alike.
Mohammed VI Green City, Marrakech
Marrakech’s Mohammed VI Green City is an example of environmentally conscious smart city planning. Energy-efficient buildings, integrated public transport systems, and renewable energy solutions are key features. The city also incorporates Moroccan architectural styles and cultural elements, ensuring that modernization does not erase the city’s historic identity. The project has become a benchmark for combining sustainability, technology, and cultural preservation.
Rabat Technopolis
Rabat’s Technopolis is a hub for research, education, and innovation. Designed to attract startups and international partnerships, it fosters a knowledge-driven economy while maintaining the city’s historic charm. Technopolis serves as a bridge between Morocco’s traditional urban identity and its modern aspirations, proving that smart cities can support economic growth without compromising heritage.
These case studies demonstrate the diversity and potential of Smart Cities in Morocco. From newly built eco-cities to innovative upgrades in historic urban centers, each project offers valuable lessons in balancing technology, sustainability, and culture. They show that Morocco is not only adopting smart city concepts but also customizing them to fit the country’s unique social and cultural context.
The Future of Smart Cities in Morocco
As Morocco continues to expand its smart city initiatives, the future promises a dynamic integration of technology, sustainability, and cultural preservation. Smart Cities in Morocco are expected to evolve with cutting-edge innovations such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G connectivity, and advanced data analytics, all aimed at creating more efficient, resilient, and livable urban environments.
AI and Predictive Urban Planning
Artificial intelligence is set to revolutionize Moroccan cities by enabling predictive urban planning. By analyzing traffic patterns, energy consumption, and population trends, AI can help city planners make informed decisions that optimize resources and reduce inefficiencies. Predictive analytics will also enhance public services, allowing authorities to anticipate issues such as traffic congestion, energy shortages, or waste management needs before they become critical.
IoT and Connected Infrastructure
The Internet of Things will be a cornerstone of Morocco’s smart city infrastructure. Connected sensors and devices can monitor everything from air quality and water usage to public transport efficiency. This real-time data allows cities to respond quickly to challenges, improve safety, and ensure sustainability. For residents, IoT integration means more convenient and responsive urban living, with smart street lighting, waste collection, and energy systems.
5G Connectivity and Digital Innovation
The rollout of 5G networks across Morocco will accelerate digital innovation, supporting high-speed communication for businesses, healthcare, education, and transportation. Enhanced connectivity will enable remote work, telemedicine, and digital learning, bridging gaps between urban and suburban areas. 5G will also support emerging technologies such as autonomous vehicles and smart traffic management systems, further enhancing urban mobility.
Sustainability and Green Technology
Future smart cities in Morocco will continue to prioritize sustainability. Solar energy, smart grids, water-efficient systems, and green architecture will reduce environmental impact while supporting urban growth. Cities like Zenata and Mohammed VI Green City serve as models for how Morocco can integrate eco-friendly solutions into modern urban development.
Morocco as a Regional Leader
By combining technological innovation with cultural preservation, Morocco has the potential to become a regional leader in smart city development. The country’s approach offers a blueprint for other African nations, demonstrating that modernization and heritage can coexist. Through investment in research, education, and public-private partnerships, Morocco is poised to create smart cities that are not only efficient and sustainable but also culturally resonant and globally competitive.
The future of Smart Cities in Morocco is a vision of harmony: cities where technology enhances daily life, sustainability protects the environment, and tradition continues to thrive. As Morocco advances toward this future, residents, investors, and visitors alike will witness urban spaces that are intelligent, innovative, and authentically Moroccan.
Conclusion:
Morocco’s journey toward Smart Cities in Morocco demonstrates how a country can embrace modern technology while preserving its rich cultural heritage. From Casablanca’s intelligent traffic systems to Zenata’s eco-friendly infrastructure, Moroccan cities are evolving into urban spaces that are efficient, sustainable, and culturally vibrant. These smart city initiatives illustrate a thoughtful balance between innovation and tradition, showing that progress does not have to come at the expense of history or identity.
As Morocco continues to integrate artificial intelligence, IoT, and renewable energy into urban planning, its cities are becoming models for smart living in Africa and beyond. Residents enjoy enhanced convenience, safety, and quality of life, while businesses benefit from streamlined services and improved connectivity. At the same time, historic architecture, medinas, and cultural traditions remain central to city life, ensuring that Morocco’s identity is never lost in modernization.
